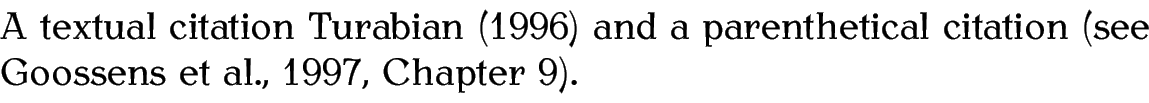5.2.1 Author-Year Citations
The default behaviour of citations with bibliography styles such as plain is to produce a numerical reference in square brackets. If you're using bibtex (rather than biblatex, described below) you can override this using a number of packages. One such package is natbib. This comes with some drop-in replacements for the standard bibliography styles: plainnat, unsrtnat and abbrvnat. The natbib package comes with a variety of package options, but I'm just going to mention a few of them: authoryear for author-year citations (default), numbers for numerical citations, super for superscripted numerical citations, round for round parentheses, square for square parentheses and sort&compress which sorts multiple citations and compresses consecutive numbers into a range. For example, [4,2,8,3] will become [2-4,8].
So for citations that give the author and year rather than a number, you need to load natbib in the preamble:
and specify one of the natbib bibliography styles:
There are two main replacements for \cite:
for textual citations and
for parenthetical citations.
Unlike \cite, these commands have two optional arguments. The
second <post> is a suffix, the same as \cite's only optional
argument. The first optional argument <pre> is a prefix. If
only one optional argument is present, it is assumed to be
<post>, so if you only want a prefix and no suffix, you have to
specify an empty argument for <post>.
Example:
(Using the same thesis-ref.bib database as earlier.)
A textual citation \citet{turabian96}
and a parenthetical citation \citep[see][Chapter
9]{goossens97}.
Result:
This book is also available as A4 PDF or 12.8cm x 9.6cm PDF or paperback (ISBN 978-1-909440-02-9).